The UK base rate history provides a detailed record of how interest rates in the United Kingdom have changed in response to economic conditions. Set by the Bank of England, the base rate influences borrowing costs, savings returns, inflation levels, and overall economic confidence. For homeowners, businesses, and investors, understanding how rates have moved in the past helps explain why financial conditions change today.
Looking back at interest rate trends also highlights how the UK economy has reacted to major global and domestic events. From inflationary pressures to financial crises and post-pandemic recovery, the uk base rate history reflects the balance the Bank of England must strike between controlling prices and supporting economic growth.
Understanding What the UK Base Rate Is
The UK base rate is the interest rate at which the Bank of England lends money to commercial banks. These banks then set their own rates for mortgages, loans, and savings based on this benchmark. As a result, even small changes to the base rate can have wide-ranging effects across the entire financial system.
When rates increase, borrowing generally becomes more expensive and spending slows, helping to reduce inflation. When rates fall, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging spending and investment. This relationship explains why the uk base rate history is closely watched by economists, policymakers, and everyday consumers.
How the UK Base Rate Has Changed Over Time
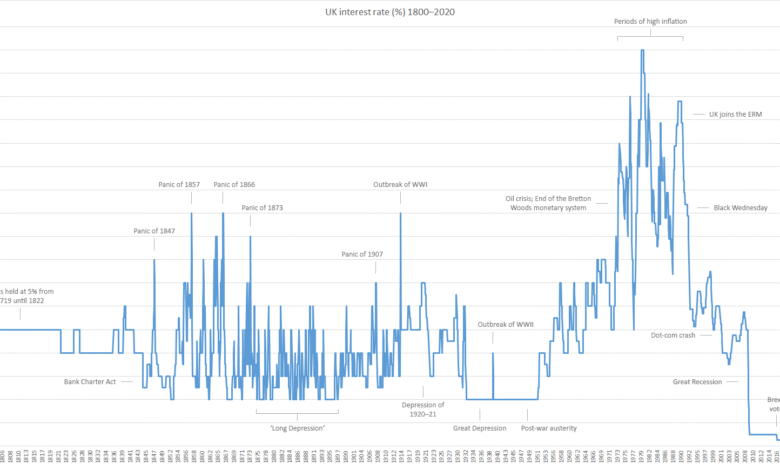
Over several decades, the uk base rate history has shown periods of extreme volatility as well as long stretches of stability. During the 1970s and 1980s, interest rates were exceptionally high due to soaring inflation and economic uncertainty. Policymakers used aggressive rate rises to protect the value of the currency and curb price growth.
In later years, particularly from the mid-1990s onwards, interest rate management became more structured with inflation targeting. This shift resulted in fewer dramatic changes and greater predictability. Studying this historical pattern helps explain why modern rate decisions tend to be more cautious and data-driven.
UK Base Rate History Chart and Graph Explained

A UK base rate history chart provides a clear visual representation of how interest rates have moved over time. Peaks on the chart often correspond with inflation crises, while deep troughs reflect recessions or periods of economic stress. These visuals make it easier to understand long-term trends rather than focusing on short-term fluctuations.
A UK base rate history graph is particularly useful for comparing different economic periods. By examining rises and falls together, readers can see how the Bank of England responds to changing conditions. Charts also help explain why some rate changes feel sudden while others occur gradually over many months.
UK Base Rate History Since 2000
Since 2000, the uk base rate history has been shaped by major global events. The early 2000s saw moderate and stable rates until the 2008 financial crisis forced the Bank of England to cut rates dramatically. This marked the beginning of a prolonged period of historically low interest rates.
Low rates were maintained for many years to encourage borrowing and economic recovery. While this helped stabilise the economy, it also reduced returns for savers and contributed to rising house prices. This era significantly altered how consumers and businesses approached debt and financial planning.
UK Base Rate History 2022 and 2023
The uk base rate history 2022 represents a sharp departure from the low-rate environment of previous years. Rapidly rising inflation, driven by global energy costs and supply chain disruption, led the Bank of England to raise interest rates multiple times in quick succession. These increases affected mortgages, rents, and business financing almost immediately.
During uk base rate history 2023, policymakers focused on controlling inflation without causing a severe economic slowdown. Rate changes became more measured, reflecting careful analysis of wage growth, consumer spending, and economic resilience. This period highlighted how responsive and adaptive modern monetary policy has become.
How UK Base Rate Changes Affect Everyday Life
Changes in the base rate directly influence household finances. Mortgage repayments often rise when rates increase, while savings accounts may offer better returns. For renters, higher borrowing costs for landlords can indirectly affect rental prices, demonstrating how base rate decisions ripple through the economy.
Businesses are also affected, as higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for expansion or investment. Understanding the uk base rate history helps individuals and companies anticipate how future changes might impact budgets, profitability, and long-term planning.
Lessons from the UK Base Rate History
One of the key lessons from the uk base rate history is that interest rates move in cycles. Periods of low rates are often followed by tightening phases when inflation rises. Recognising these cycles can help consumers make better financial decisions, such as choosing between fixed and variable borrowing options.
History also shows that economic shocks can lead to rapid policy shifts. While no one can predict future rates with certainty, understanding historical trends provides valuable context. It allows readers to interpret current decisions with greater confidence and realism.
Conclusion
The uk base rate history offers a comprehensive view of how the UK economy has evolved over time. Each rate change reflects broader economic challenges, from inflation control to crisis management and recovery. By studying these patterns, readers gain a deeper understanding of today’s financial environment.
Whether you are a homeowner, saver, or business owner, understanding past interest rate behaviour helps inform future decisions. The base rate remains one of the most powerful tools in UK economic policy, and its history continues to shape financial outcomes across the country.